5 Technology-Based Agricultural Solutions and Their Implementation Examples
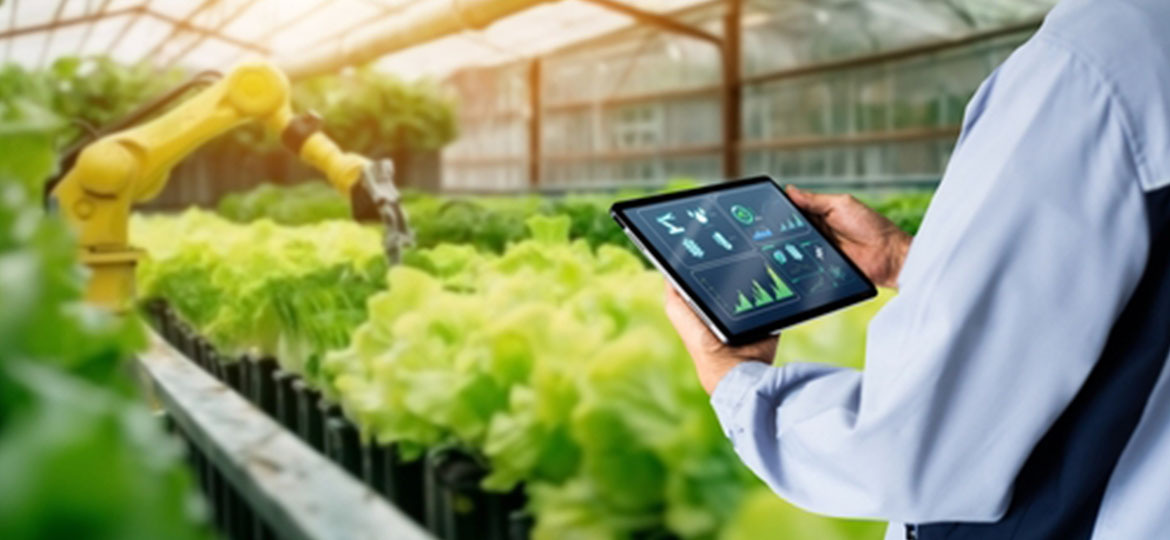

echnology-based agriculture, commonly referred to as “smart farming,” is an innovative approach that leverages digital technologies to enhance efficiency and productivity in the agricultural sector. With the global population increasing and the demand for food rising, integrating technology into farming has become crucial.
Technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), the Internet of Things (IoT), big data, and drones have revolutionized how farmers grow, manage, and harvest crops. This article explores various technology-based agricultural solutions and their real-world implementations.
1. Precision Agriculture
Precision agriculture is a method that uses technology to monitor and manage farmland in detail, based on specific data from each area of the field. This approach employs sensors, GPS, and analytical software to assist farmers in planting, fertilizing, and managing water resources more effectively.
Examples of Implementation:
- Smart Fertilization Systems: By utilizing soil sensors and analytical software, farmers can assess soil nutrient levels and tailor their fertilizer application to the specific needs of each field area. This approach optimizes fertilizer use, reduces costs, and minimizes environmental impact caused by excessive fertilizer application.
- Targeted Irrigation: Soil moisture sensors and automated irrigation systems enable farmers to deliver water only to areas that need it, reducing water waste. This technology is particularly effective in drought-prone regions, improving crop yields with minimal water usage.
2. Drones for Crop Spraying and Monitoring
Drones have become a widely used technological solution in modern agriculture, especially for monitoring crop conditions and spraying pesticides or fertilizers. They allow for extensive monitoring in a short time and provide detailed visual insights into field conditions.
Examples of Implementation:
- Field Condition Monitoring: Equipped with multispectral cameras, drones can detect the health of crops, such as signs of disease or nutrient deficiencies. The data is analyzed by systems that provide actionable recommendations for farmers to take preventive measures.
- Precision Spraying of Fertilizers and Pesticides: Drones can precisely apply fertilizers and pesticides to specific areas, ensuring that each section receives the required amount. This not only enhances spraying efficiency but also reduces environmental impact compared to traditional manual spraying methods.
3. IoT for Monitoring Fields and Crop Conditions
IoT (Internet of Things) technology enables devices on farms to connect to the internet and transmit data. IoT systems collect data from various sensors installed on farmland, such as soil moisture, temperature, air humidity, and soil pH sensors.
Examples of Implementation:
- Soil Condition Monitoring: IoT sensors measure real-time soil moisture and quality. This information is transmitted to farmers' devices or management centers, allowing them to assess soil conditions across different field sections and take quick actions if needed.
- Storage Management: IoT sensors are also used in storage facilities to monitor temperature and humidity levels. This data helps farmers maintain optimal storage conditions, preventing spoilage and ensuring crop quality before distribution.
4. AI for Agricultural Analysis and Predictions
AI plays a significant role in agriculture by helping farmers predict weather patterns, determine the best planting times, and estimate productivity levels. AI analyzes large datasets from various sources, including weather data, soil conditions, and historical records, to provide optimal recommendations for farmers.
Examples of Implementation:
- Harvest Predictions: Using weather data, historical trends, and current crop conditions, AI can predict the best harvest times. This helps farmers manage labor and equipment more efficiently.
- Early Disease Detection: AI is also used to identify plant diseases early through image analysis. AI-powered applications can process images of crops captured by drones or cameras and detect early signs of disease, such as changes in leaf color or shape. Early detection allows farmers to act quickly to prevent disease spread.
5. Autonomous Tractors and Machinery
Modern tractors and autonomous agricultural machines represent technological advancements that enable equipment to operate without human supervision. These tools are equipped with GPS, sensors, and AI, allowing them to work independently on farms. Autonomous machinery can perform tasks such as planting, harvesting, and spraying fields automatically, reducing the reliance on manual labor.
Examples of Implementation:
- Automatic Planting and Fertilizing: Autonomous machines with GPS and sensors can plant seeds precisely and apply the correct amount of fertilizer to each section of the field. This reduces planting and fertilizing errors, resulting in optimal and uniform crop yields.
- Automated Crop Maintenance: In addition to planting, autonomous machines can perform maintenance tasks such as pesticide spraying and crop pruning. These machines save time and costs while delivering consistent results by adhering to preset parameters.
By implementing these technology-based agricultural solutions, farmers can significantly enhance productivity, efficiency, and sustainability. Hopefully, this information will inspire further innovations and applications in the agricultural sector.
Other News